PDI AEL Spark Version 8 Improvements
At Pentaho World 2017 following improvements were mentioned (Source):
- Communicates with Pentaho client tools over WebSocket; does NOT require Zookeeper
- Uses distro-specific Spark library
- Enhanced Kerberos impersonation on client-side
This brings a bunch of benefits:
- Reduced number of steps to setup
- Enable fail-over, load-balancing
- Robust error and status reporting
- Customization of Spark jobs (i.e. memory , settings)
- Client to AEL connection can be secured
- Kerberos impersonation from client tool
Other improvements:
- Big Data File Formats - Avro and Parquet steps: When you run in AEL, these will also be natively interpreted by the engine, which adds a lot to the value of this.
Other notes:
- There is still no improvement on the Group By step. Basically, everything still has to go via a single node (Spark client) - there is no proper Spark support to run it in parallel.
- There is no support in AEL Spark Streaming for event time in a windowing function. Windowing can be achieved (as highlighted in Pedro’s blog) by using a sub-transformation (you can define the batch interval in the job entry settings) and then you can do the aggregation in the sub-transformation based on processing time (not event, not ingestion time).
- Spark client: Is there still a limitation to run it on the edgenode? Yes.
Official Documentation:
- Pentaho v8: Set Up the Adaptive Execution Layer (AEL)
Setup for v8
Spark Client
If not already installed on your local machine, download the Spark Client from here.
The environment variable SPARK_HOME will point to the Spark Client folder.
PDI
PDI Download:
- PDI-CE v8.0 from here.
Unzip it and move the folder to a convenient location. Make the shell files executable.
Configuration
Local Setup for Development
The exciting news in PDI v8 is that Pentaho took all the complexity out of the local setup! It is really easy now to get going with PDI and Spark!
AEL Daemon: The Adaptive Execution Layer is part of the PDI client now! You can find it in the adative-execution folder within <pdi-client-root>. The environment variable PDI_AEL_DAEMON_HOME will point not to this folder but the parent folder, which is <pdi-client-root>.
Adjust the configuration of the AEL Daemon by adjusting this file:
data-integration/adaptive-execution/config/application.properties
Change the following properties:
| property | value | environment variable |
|---|---|---|
sparkHome |
path your local Spark client | SPARK_HOME |
sparkApp |
path to your AEL Daemon data-integration folder |
PDI_AEL_DAEMON_HOME |
hadoopConfDir |
path to directory containing all the Hadoop config details (*-site.xml) |
HADOOP_CONF_DIR |
Here is my example configuration with hard-coded values (import bits shown only):
# Hadoop Configuration
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Directory where *-site.xml files reside for Hadoop Configuration
hadoopConfDir=/home/dsteiner/apps/hadoop-2.8.0/etc/hadoop
# Hadoop User which will run job
hadoopUser=dsteiner
# Spark Configuration
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Location of Apache Spark Client distribution\
sparkHome=/home/dsteiner/apps/spark-2.1.0-bin-hadoop2.7
# Spark Master
# Where spark will run: local / yarn
# Note, you can also simulate multiple executors by using this notation (i.e. 2 executors): local[2]
sparkMaster=local[2]
# Deploy Mode
# This property is only used when the master is set to `yarn`.
# client - Driver will run on the daemon machine; but the executors will run in Yarn
# cluster - Entire application will be run in cluster (Not supported yet)
sparkDeployMode=client
# AEL Spark Properties
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Main PDI Driver location (can be pdi-ee-client or pdi-spark-driver)
sparkApp=/home/dsteiner/apps/pdi-ce-8.0
Alternatively, if you set the environment variables in bashrc (in example):
export HADOOP_CONF_HOME=<your-value>
export SPARK_HOME=<your-value>
export PDI_AEL_DAEMON_HOME=<your-value>
You can reference them inside the config like so:
# Hadoop Configuration
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Directory where *-site.xml files reside for Hadoop Configuration
hadoopConfDir=${HADOOP_CONF_DIR}
# Hadoop User which will run job
hadoopUser=dsteiner
# Spark Configuration
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Location of Apache Spark Client distribution\
sparkHome=${SPARK_HOME}
# Spark Master
# Where spark will run: local / yarn
# Note, you can also simulate multiple executors by using this notation (i.e. 2 executors): local[2]
sparkMaster=local[2]
# Deploy Mode
# This property is only used when the master is set to `yarn`.
# client - Driver will run on the daemon machine; but the executors will run in Yarn
# cluster - Entire application will be run in cluster (Not supported yet)
sparkDeployMode=client
# AEL Spark Properties
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Main PDI Driver location (can be pdi-ee-client or pdi-spark-driver)
sparkApp=${PDI_AEL_DAEMON_HOME}
Next create a directory called kettleConf inside your Spark Client’s root directory:
cd $SPARK_HOME
mkdir kettleConf
Note: If the
kettleConffolder already exists and has a few files in it, it is probably best to remove these files.
Note: The Spark Client will be called by PDI, so you do not have to start it independently. Nothing to do. Simple.
Next start the AEL Daemon like so:
cd $PDI_AEL_DAEMON_HOME
# run as foreground process - great for debugging
sh ./daemon.sh
# or start as a background process
sh ./daemon.sh start
# check the status if in background mode
./daemon.sh status
Create Run Configuration
Now that the AEL Daemon is running, we can create a Run Configuration in Spoon. You can think of this as configuring just another engine to run your jobs or transformations with.
Setting up a Run Configuration in Spoon is very easy:
- Go to the View tab.
- Right click on Run configurations and choose New.
- In the Run configuration dialog provide a name and description. As Engine choose
Spark. The default connection entries should be just fine for your local setup (http://127.0.0.1:53000).
Note: You might wonder what port
53000relates to? This is the port defined for the AEL Deamon inadaptive-execution/config/application.properties.
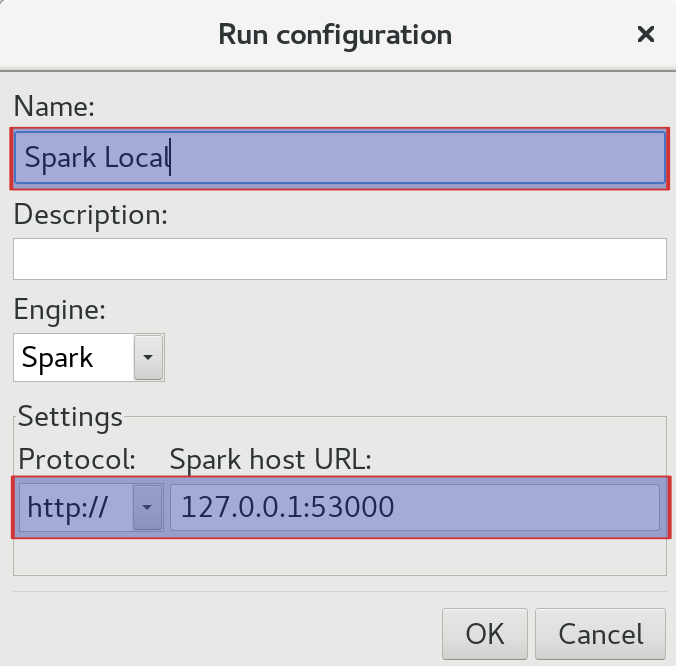
When you execute your job or transformation next time, pick this Run Configuration.
FAQ
- Q: Does the Spark client or server have to be running for PDI AEL to work? A: No. PDI AEL will start the Spark Client by itself.
- Q: Is it necessary to have Spark set up to connect to HDFS? A: No. If you want to run Hadoop specific steps/job entries,
sparkMastermust be set toyarn. You can simulate this locally by running a pseudo-distributed Hadoop cluster. If you want to do this, configure the AEL Daemon as shown in the next section and also upload pdi-spark-executor.zip` to HDFS. - Q: Is it necessary to have HDFS running? A: No, unless you changed the AEL Daemon config so that everything runs against YARN.
Spark Logging
One of the great things about AEL is that the essential logs are available straight in Spoon/PDI. You remember Pentaho Map/Reduce? Yes - then you might remember that you actually had to get the logs from YARN to understand what was going on.
While AEL has you covered on the logging side, you might still be extremely curious and want to see the full Spark logs. Here is the pro-tip from Matt Campell:
For spark logging, the trick is to first set
overwriteConfig=false
in the daemon’s config/application.properties file.
Important: Make sure you restart the deamon after changing the config.
This will allow the $SPARK_HOME/kettleConf/spark-defaults.conf file to persist across executions. You can then set spark logging (and any other spark props of interest):
spark.eventLog.enabled=true
spark.eventLog.dir=/tmp/spark.log
Running on the Cluster (YARN Mode)
Note: There is no dependency any more on Zookeeper in v8.
This is configuration for the production environment. You can also use it locally if you are running a pseudo-distributed cluster.
Spark Application
Since some users extend the PDI core functionality by additional steps (plugins) e.g. from the Marketplace, not every PDI setup is the same. We will have to make the essential libraries of our possibly customised PDI setup available to the Spark cluster via building an zip file which bundles any dependencies (libraries). If you’ve every written a plain Scala or Java Scala app and then created an uber jar, this will all sound quite familiar to you.
PDI comes with the Spark Application Builder Tool, which we will use to create this zip file (called pdi-spark-driver.zip). To be precise, the zip file has two essential contents:
data-integration: This looks pretty much like your local PDI client installationpdi-spark-executor.zip: bundles all the required PDI libraries, so that it can be distributed on the Spark cluster.
The idea is that you copy pdi-spark-driver.zip to an edgenode on your cluster and extract it there.
If you are just planning to do local development, you can unzip pdi-spark-driver.zip locally as well.
And this how your create the zip file on Linux:
Note: Currently there is still a bug open that the Spark App Builder script expects the parent folder to be called
data-integration. When you unzip the downloaded PDI zip file, by default the extracted folder will be calleddata-integration, however, when you have more than one version on your system, then some people tend to rename this folder. If you are one of these people, you will have to rename the folder temporarily.
# if you renamed the PDI root folder, change it back to it's original name temporarily
mv pdi-ce-8.0 data-integration
cd data-integration
sh ./spark-app-builder.sh -outputLocation /tmp
cd ..
mv data-integration pdi-ce-8.0
Configuration
If you intend to use with Spark and YARN on the cluster, the following additional steps are necessary:
Add following variables to bashrc (in example):
export HADOOP_CONF_HOME=<your-value>
export SPARK_HOME=<your-value>
export PDI_AEL_DAEMON_HOME=<your-value>
export HDFS_SPARK_EXECUTOR_LOCATION=<your-value>
Copy pdi-spark-driver.zip to the edge node and unzip the file. As mentioned before, you will find a data-integration folder and the pdi-spark-executor.zip inside the extracted folder.
Adjust the configuration of the AEL Daemon by adjusting this file:
data-integration/adaptive-execution/config/application.properties
Change the following properties:
| property | value | environment variable |
|---|---|---|
sparkHome |
path your local Spark client | SPARK_HOME |
sparkApp |
path to your AEL Daemon data-integration folder |
PDI_AEL_DAEMON_HOME |
hadoopConfDir |
path to directory containing all the Hadoop config details (*-site.xml) |
HADOOP_CONF_DIR |
hadoopUser |
user id which submits the PDI Spark job. Only applicable if you are not using security | |
sparkMaster |
yarn |
|
| assemblyZip | hdfs:$HDFS_SPARK_EXECUTOR_LOCATION |
HDFS_SPARK_EXECUTOR_LOCATION |
My configuration looked like this (partially shown only, local setup with a pseudo distributed cluster):
# Hadoop Configuration
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Directory where *-site.xml files reside for Hadoop Configuration
#hadoopConfDir=${HADOOP_CONF_DIR}
hadoopConfDir=/home/dsteiner/apps/hadoop-2.8.0/etc/hadoop
# Hadoop User which will run job
hadoopUser=dsteiner
# Spark Configuration
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Location of Apache Spark Client distribution\
#sparkHome=${SPARK_HOME}
sparkHome=/home/dsteiner/apps/spark-2.1.0-bin-hadoop2.7-yarn
#sparkHome=/home/dsteiner/apps/spark-2.2.0-bin-hadoop2.7-standalone
# Spark Master
# Where spark will run: local / yarn
# Note, you can also simulate multiple executors by using this notation (i.e. 2 executors): local[2]
#sparkMaster=local[2]
sparkMaster=yarn
# Deploy Mode
# This property is only used when the master is set to `yarn`.
# client - Driver will run on the daemon machine; but the executors will run in Yarn
# cluster - Entire application will be run in cluster (Not supported yet)
sparkDeployMode=client
# AEL Spark Properties
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Main PDI Driver location (can be pdi-ee-client or pdi-spark-driver)
#sparkApp=${PDI_AEL_DAEMON_HOME}
sparkApp=/home/dsteiner/apps/pdi-ce-8.0
sparkAppClass=org.pentaho.pdi.spark.driver.SparkWebSocketMain
# Spark Assembly Zip
# This is the zip file of the PDI Assembly that will be used on the executors.
# It is recommended to leverage an HDFSreference which will help with performance launching the application.
assemblyZip=hdfs:/opt/pentaho/pdi-spark-executor.zip
Next create a directory called kettleConf inside your Spark Client’s root directory:
cd $SPARK_HOME
mkdir kettleConf
Copy pdi-spark-executor.zip to HDFS and extract the contents. This location is referred to as HDFS_SPARK_EXECUTOR_LOCATION.
cd /tmp
unzip pdi-spark-driver.zip
hdfs dfs -put ./pdi-spark-executor.zip /opt/pentaho
Note: If you’ve previously uploaded a PDI Spark Executor to HDFS, make sure you remove it first.
Next start the AEL Daemon like so:
cd $PDI_AEL_DAEMON_HOME
sh ./daemon.sh
# or start as a background process
sh ./daemon.sh start
# check the status if in background mode
./daemon.sh status
YARN Resource Manager UI and YARN Command Line Client
When you run your PDI jobs via AEL Spark, you have at least 3 ways to check what’s going on:
- PDI logs: Utterly convient, PDI logs will show you the work that is going on on the Spark cluster as well.
- Yarn Resource Manager Web UI: Head over to
http://localhost:8088/cluster(or similar) and check what’s going on (you can also get hold of the logs here):
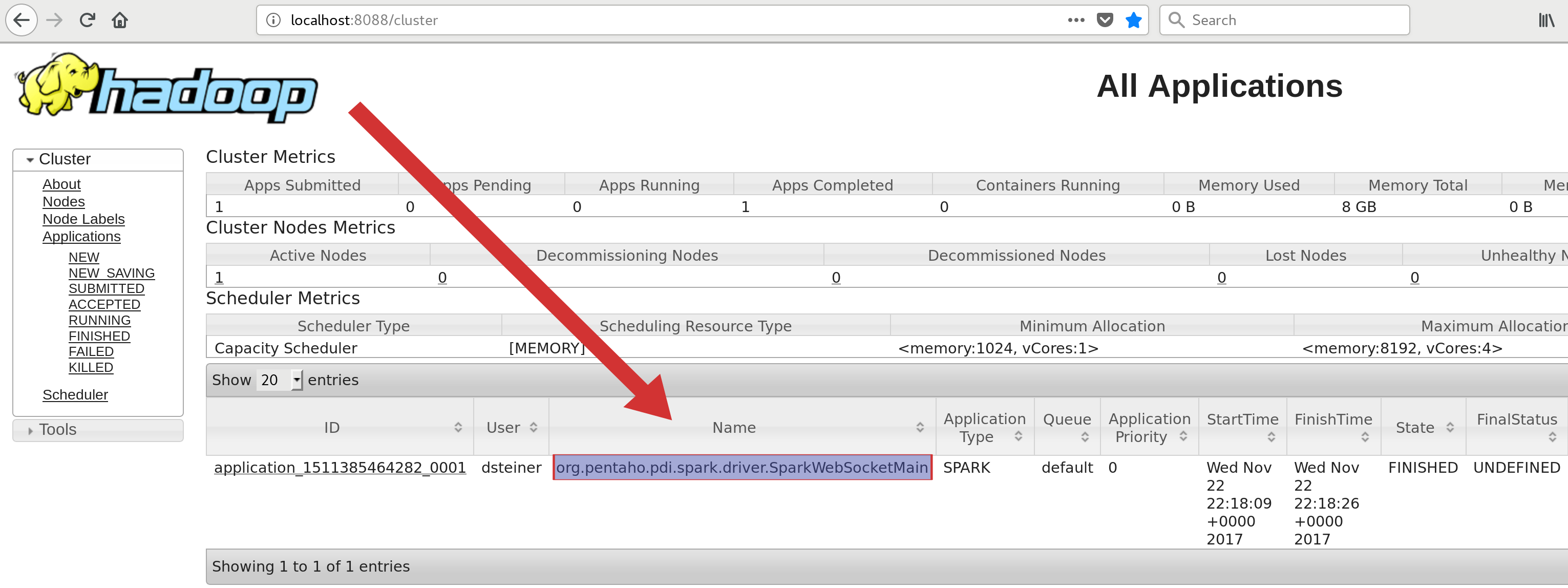
- Yarn Command Line Client:
$ yarn application -list -appStates ALL
17/11/22 22:30:06 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at localhost/127.0.0.1:8032
Total number of applications (application-types: [] and states: [NEW, NEW_SAVING, SUBMITTED, ACCEPTED, RUNNING, FINISHED, FAILED, KILLED]):1
Application-Id Application-Name Application-Type User Queue State Final-State Progress Tracking-URL
application_1511385464282_0001 org.pentaho.pdi.spark.driver.SparkWebSocketMain SPARK dsteiner default FINISHED UNDEFINED 100% N/A
Then you can get the log by specifying the application id that the previous command returned:
yarn logs -applicationId application_1511385464282_0001 | less
Securing AEL Spark
Take a look at the info provided here
Steps that do not run in parallel
A list of EE supported steps which cannot be run in parallel and hence have to be executed on a single node can be found in:
<pdi-root>system/karaf/etc/org.pentaho.pdi.engine.spark.cfg
All the data will be moved to this single node (the Spark client) and the process will be executed in a single thread. Since the Spark Client can currently only run outside the cluster on an edgenode, and for some steps this means that all the data has to leave the cluster and travel to the edgenode for processing and then possibly back again to the cluster.
You can extend this list with any other plugins that you use, which cannot run in parallel.
- Abort
- AccessInput
- AccessOutput
- AutoDoc
- BlockingStep
- BlockUntilStepsFinish
- ClosureGenerator
- ConcatFields
- CsvInput
- CubeInput
- CubeOutput
- DataGrid
- Delete
- Denormaliser
- DetectLastRow
- ExcelInput
- ExcelOutput
- FieldsChangeSequence
- FixedInput
- Flattener
- Flatterner
- GetFileNames
- GetFilesRowsCount
- GetRepositoryNames
- GetSubFolders
- GetTableNames
- getXMLData
- GroupBy
- HL7Input
- InsertUpdate
- JmsInput
- JmsOutput
- JsonInput
- JsonOutput
- LDAPInput
- LDAPOutput
- LDIFInput
- LoadFileInput
- MailInput
- MemoryGroupBy
- MondrianInput
- MQInput
- MQOutput
- OlapInput
- ParallelGzipCsvInput
- PentahoReportingOutput
- PropertyInput
- PropertyOutput
- RandomCCNumberGenerator
- RandomValue
- RowGenerator
- RssInput
- RssOutput
- S3CSVINPUT
- S3FileOutputPlugin
- SalesforceDelete
- SalesforceInput
- SalesforceInsert
- SalesforceUpsert
- SAPINPUT
- SASInput
- Sequence
- ShapeFileReader
- SQLFileOutput
- SynchronizeAfterMerge
- SystemInfo
- TableInput
- TableOutput
- TypeExitExcelWriterStep
- TypeExitGoogleAnalyticsInputStep
- Unique
- UniqueRowsByHashSet
- Update
- XBaseInput
- XMLInputStream
- XMLOutput
- YamlInput
Jira Cases Filed
- AEL Spark: Support for Event Time and Windowed Aggregations
- AEL: Add option to Spark Appliation Builder to build Uber Jar only
- AEL Spark: Support to run Group By in Parallel
- AEL Daemon: Check Config on Startup
- AEL Spark: The startup time is too long
- AEL Spark: Kerberos and Pentaho Server Error
Update: PDI v8.1
- Group By step runs on Spark natively now.
- Add any Spark properties directly to the
application.propertiesfile or transformation parameters to make this easier.
